Zhenmushou (Two-headed antlered tomb guardian figure)
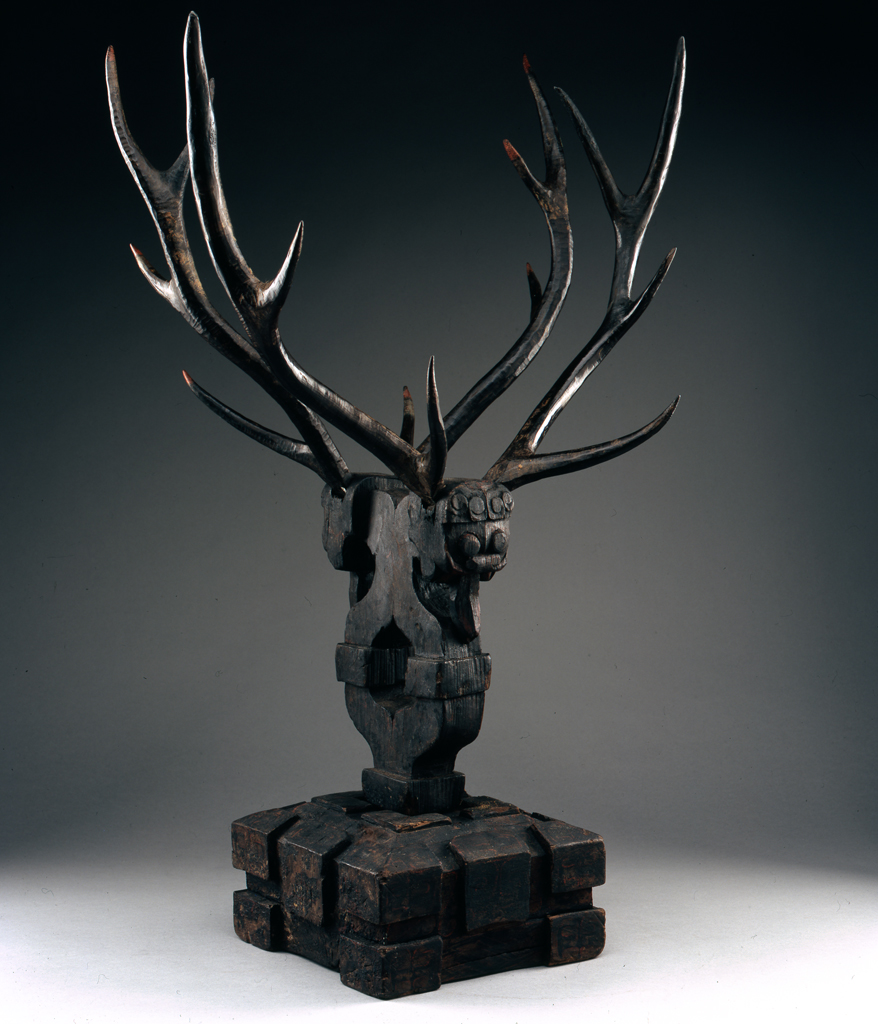

China, Jiangling Chu culture, Hubei province, Zhenmushou (Two-headed antlered tomb guardian figure), 4th century BCE/3rd century BCE, wood with traces of red and black lacquer; natural antlers with traces of vermillion lacquer, The Arlene and Harold Schnitzer Collection of Early Chinese Art, public domain, 2002.71.1a-e









This work is not currently on view.
- Title
Zhenmushou (Two-headed antlered tomb guardian figure)
- Related Titles
display title: Zhenmushou (Two-headed tomb guardian)
original language: 彩繪漆木雙頭鎮墓獸
original language: 彩繪漆木雙頭鎮墓獸 中國湖北江陵 戦國・楚文化
translated: Two-headed tomb guardian
transliterated: Zhenmushou
- Artist
- Date
4th century BCE/3rd century BCE
- Period
China: Warring States period (475-221 BCE)
- Medium
wood with traces of red and black lacquer; natural antlers with traces of vermillion lacquer
- Dimensions (H x W x D)
38 in x 25 3/4 in x 18 in
- Collection Area
Asian Art
- Category
Sculpture
- Object Type
funerary sculpture
figurine
- Culture
Chinese
- Credit Line
The Arlene and Harold Schnitzer Collection of Early Chinese Art
- Accession Number
2002.71.1a-e
- Copyright
public domain
- Terms
Antlered guardian figures are unique to tombs of the Chu culture, which flourished in south central China from the 7th to the 2nd centuries BCE. Double-headed guardian figures, like this one, were for tombs of the elite, while single-headed guardians were for those of lower rank. Their function is unknown, but they may have been used in shamanistic rituals during the tomb occupant’s lifetime or during the funeral.
- Exhibitions
2005 Mysterious Spirits, Strange Beasts, Earthly Delights: Early Chinese Art from the Arlene and Harold Schnitzer Collection Portland Art Museum
2012 Cornerstones of a Great Civilization: Masterworks of Ancient Chinese Art Portland Art Museum